Types of Problem Solving
MCAT Psychology - Chapter 2- Section 4 - Cognition - Intelligence & Problem-Solving
- Home
- »
- MCAT Masterclass
- »
- Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior
- »
- Psychology
- »
- Cognition
- »
- Intelligence and Problem-Solving
- »
- Types of Problem Solving – MCAT Psychology
Sample MCAT Question - Types of Problem Solving
Which of the following involves inducing structure problem solving?
a) Anagrams
b) Series Completion
c) Tower of Hanoi
d) All of the above
B is correct.
In series completion, a problem solver must determine the next item in a series. This is an example of inducing structure, which requires the problem solver to identify the relations or patterns between items in the problem. Therefore, series completion is the correct answer. Answer choice A is incorrect because anagram, which is a type of problem that involves rearranging letters to form a word, is an example of arrangement. Arrangement is a type of problem solving in which the problem solver must arrange different objects in a specific way that satisfies some criterion. Answer choice C is incorrect because the Tower of Hanoi problem is an example of transformation. Transformation is a type of problem solving in which the problem solver must carry out a sequence of transformations in order to complete a specified goal.
Conciousness-Altering Drugs
Get 1-on-1 MCAT Tutoring From a Specialist
With MCAT tutoring from MedSchoolCoach, we are committed to help you prepare, excel, and optimize your ideal score on the MCAT exam.
For each student we work with, we learn about their learning style, content knowledge, and goals. We match them with the most suitable tutor and conduct online sessions that make them feel as if they are in the classroom. Each session is recorded, plus with access to whiteboard notes. We focus on high-yield topics if you’re pressed for time. If you have more time or high-score goals, we meticulously cover the entire MCAT syllabus.
Types of Problem Solving for the MCAT
Understanding the psychological aspects of problem-solving is a critical part of MCAT preparation. This article explores several facets of problem-solving that are pertinent to your MCAT studies, focusing on three principal types: inducing structure, arrangement, and transformation.
Inducing Structure
One type of problem-solving is inducing structure, which involves a person identifying the relations or patterns between the items in a problem. There are many types of problems that involve inducing structure. An example of an inducing structure problem is series completion, where a number of items in a series are presented in a specific order. These problems typically involve identifying a pattern and determining the next item in the series. For example, consider the series: 1, 2, 3, 9, 4, 5, 6, 6. This series is counting up like 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and in between these numbers are 9 and 6, which are decreasing by three. Based on this, what comes next in the sequence would be continuing to count up: 7, 8, 9. Then, since 9 and 6 are decreasing by three, the number 3 should come next: 1, 2, 3, 9, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 3. Another example is the series: A5E9. The transition from A to E is four letters, and the transition from 5 to 9 is four numbers. The letters and numbers should be expected to continue by 4, so the continued series should read: A5E9I13.
Another type of inducing structure is analogy problems, which involve being given an example of a relationship and then applying it to a new situation or topic. An example of an analogy is, “grocery market is to fruits and vegetables, as pharmacy is to: what?” First, the relationship between a grocery market and fruits and vegetables must be determined. Grocery markets sell fruits and vegetables. Pharmacies sell medication, which would be the answer to the analogy. Another example of an analogy is, “salesperson is to client, as physician is to: what?” Salespersons work with clients, and physicians work with patients, which would be the answer to this analogy.
Arrangement
Another type of problem-solving is arrangement. In problems of arrangement, different objects must be arranged in a specific way to satisfy some criteria. The objects can be arranged in many ways, but only one or a few arrangements form a solution.
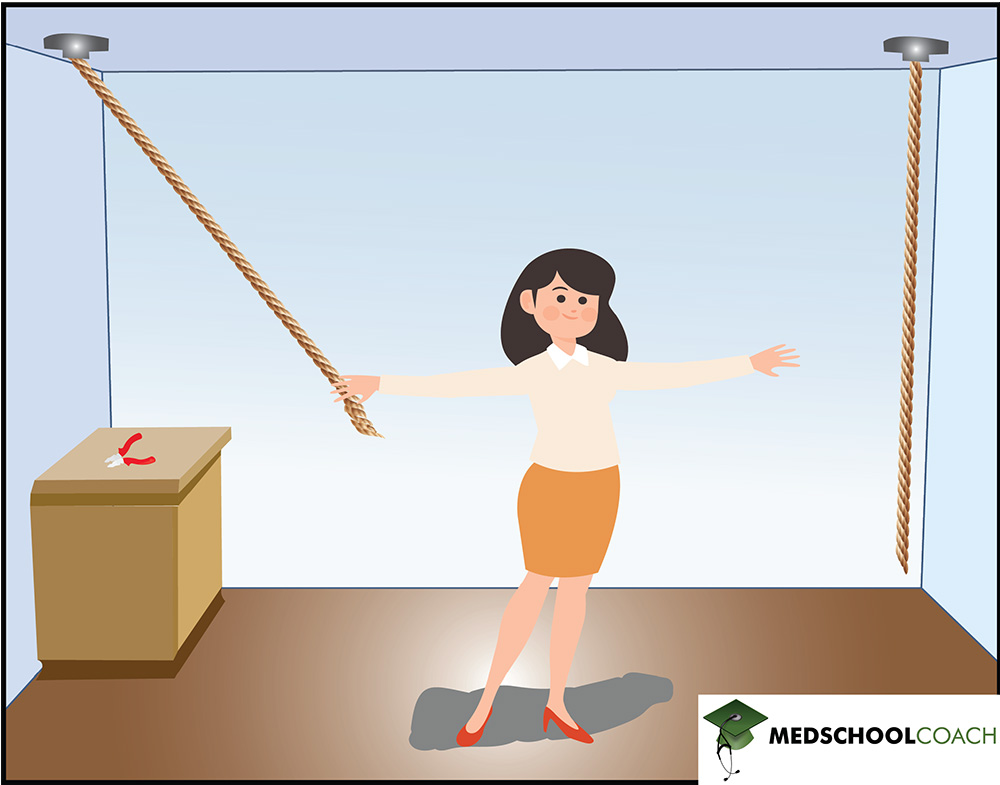
An example of an arrangement problem is anagrams. In anagrams, several letters can be rearranged to make a word. For example, K, J, I, C, H, and A can be rearranged to form the word ‘hijack.’ Y, Y, A, A, N, and W can be rearranged to form the word ‘anyway.’ Another example of an arrangement problem is known as the String Problem, which is depicted in Figure 1. Two strings hanging from a ceiling need to be tied together. However, they are so far apart that when a person grabs one string, they are too far away to grab the other. On a table, there is a pair of pliers, and the problem requires determining how to tie the strings together with the given materials.
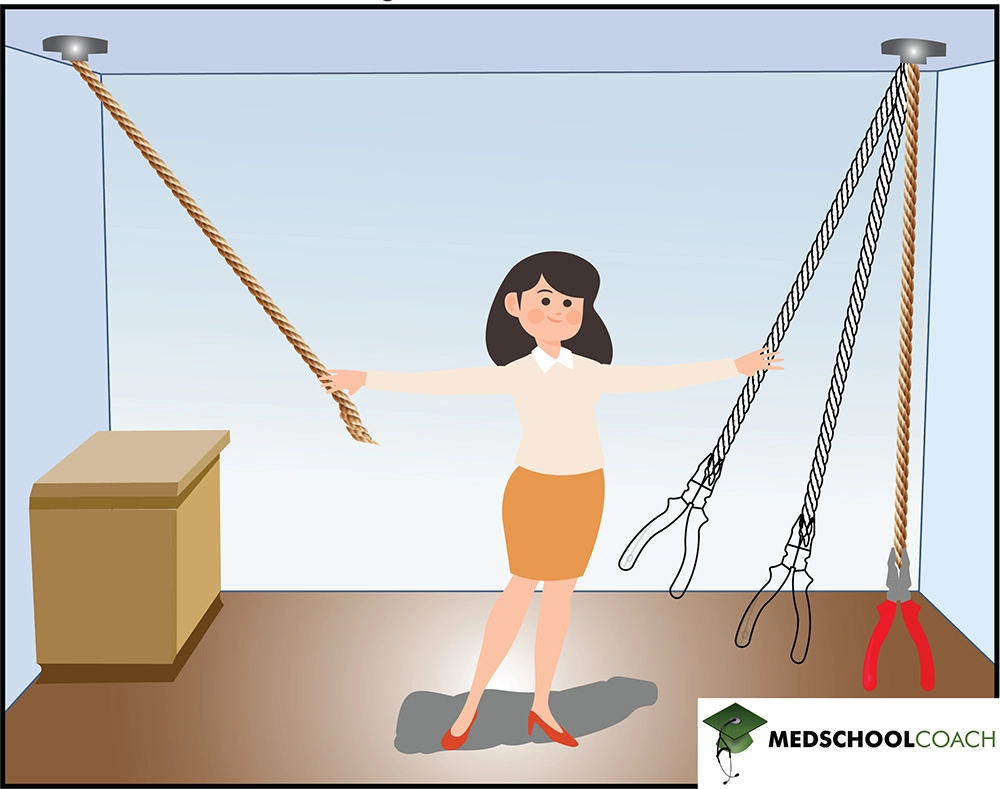
As seen in Figure 2, the solution to this problem is to take the pliers and tie it to one of the strings to create a pendulum. As you are holding one string, the pliers can swing towards you in the air like a pendulum, allowing you to grab the other string and tie the two strings together. The String Problem demonstrates how the arrangement of objects in a specific way can facilitate problem-solving.
Transformation
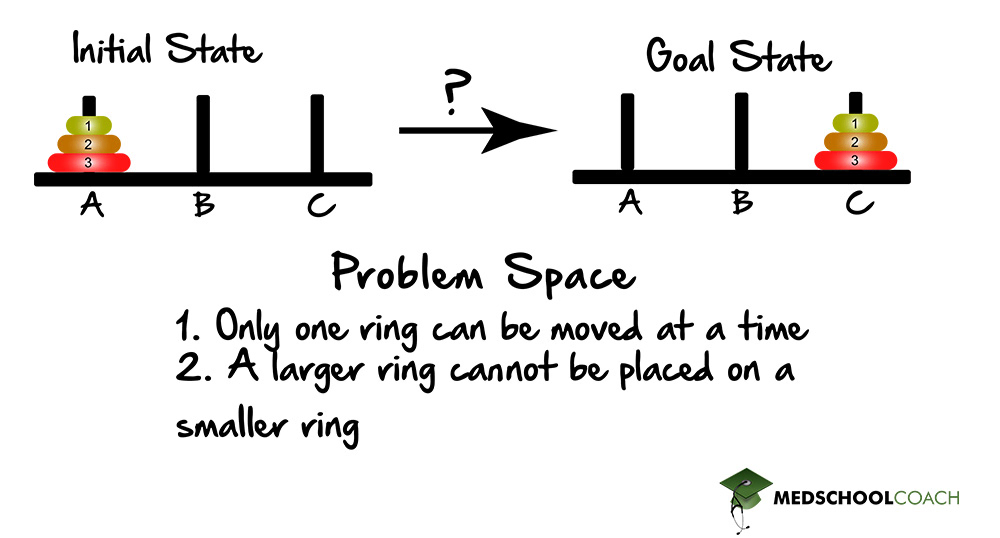
Another type of problem-solving is problems of transformation, where a sequence of transformations must be carried out in order to complete a specified goal. These problems involve an initial state, a goal state, and a problem space that describes all possible maneuvers. An example is the Tower of Hanoi, which is depicted in Figure 3. There are three pegs: A, B, and C. Initially, there are usually three rings on Peg A, with the largest ring on the bottom and the smallest ring on the top. This represents the initial state. The goal state is to have the same three rings on Peg C. To get from the initial state to the goal state, the rings can be moved. However, only one ring can be moved at a time, and a larger ring cannot be placed on a smaller ring. The possible maneuvers that can be carried out represent the problem space.
Another example of a problem of transformation is the Water Jug Problem, where there is a 37 cup jar, a 12 cup jar, and a five cup jar. These three jars are initially empty, but water can be drawn and discarded from these jars an infinite number of times. The goal is to measure out exactly 10 cups of water, but none of the jars can hold exactly 10 cups of water; the jars must be used in some way to get exactly 10 cups of water. This problem can be approached by representing each jar as a letter: the 37 cup jar is A, the 12 cup jar is B, and the five cup jar is C. A can be filled to hold 37 cups of water. This can be poured into B, getting rid of 12 cups of water and leaving A with 25 cups of water. If this is now poured into C, it removes another five cups of water. If A is poured into C three times, it will remove 15 cups of water and leave A with 10 cups of water. The Tower of Hanoi and Water Jug Problems are transformation problems because they require a certain sequence of transformations to be performed to go from the initial state to the goal state.
Explore More MCAT Masterclass Chapters
Take a closer look at our entire MCAT Masterclass or explore our Biochemistry lessons below.

One-on-One Tutoring
Are you ready to take your MCAT performance to a whole new level? Work with our 99th-percentile MCAT tutors to boost your score by 12 points or more!
See if MCAT Tutoring can help me
Talk to our enrollment team about MCAT Tutoring

MCAT Go Audio Course
Engaging audio learning to take your MCAT learning on the go, any time, any where. You'll be on the way to a higher MCAT score no matter where you are. Listen to over 200+ lessons.
MCAT Practice Exams
Practice makes perfect! Our mock exams coupled with thorough explanations and in-depth analytics help students understand exactly where they stand.
MCAT Prep App
Access hundreds of MCAT videos to help you study and raise your exam score. Augment your learning with expert-created flashcards and a question banks.