The Excretory System & Kidneys
MCAT Biology - Chapter 7 - Section 7.1 - Organ Systems - Excretory System
- Home
- »
- MCAT Masterclass
- »
- Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems
- »
- Biology
- »
- The Excretory System & Kidneys – MCAT Biology
Sample MCAT Question - The Excretory System & Kidneys
Which of the following is a major function of the kidneys?
a) Pumps blood through the entire body
b) Removes old red blood cells from circulation
c) Maintains blood volume and composition
d) Breaks down insulin and other hormones
C is correct. Maintains blood volume & composition. The kidney can act in various capacities performing several different vital biological functions. One of the functions of the kidney is to maintain the volume and composition of blood. For example, if the blood volume in the body is too low, as in dehydration, the kidneys will decrease urine output to help regulate and maintain a healthy blood volume. Likewise, if the blood volume is too high, the kidneys will increase the volume of urine. Answer choices A and B are incorrect and describe the heart. Answer choice D is incorrect because while kidney cells may break down some hormones, this is not a major function.
Get 1-on-1 MCAT Tutoring From a Specialist
With MCAT tutoring from MedSchoolCoach, we are committed to help you prepare, excel, and optimize your ideal score on the MCAT exam.
For each student we work with, we learn about their learning style, content knowledge, and goals. We match them with the most suitable tutor and conduct online sessions that make them feel as if they are in the classroom. Each session is recorded, plus with access to whiteboard notes. We focus on high-yield topics if you’re pressed for time. If you have more time or high-score goals, we meticulously cover the entire MCAT syllabus.
Introduction to the Excretory System & Kidneys
In this MCAT post, we’ll be introducing you to the excretory system, one of the major organ systems of the human body. We’ll discuss both the anatomy of the excretory system as well as its function in the body. Then we’ll zero in on the kidneys specifically, as these are the most important organs in the excretory system. We’ll discuss the unique anatomy of the kidneys, as well as the various roles they play in maintaining the health of the organism.
Anatomy and Function of the Excretory System
The excretory system is a biological system that removes waste from the body and helps to maintain internal homeostasis. It is a complex system that consists of many structures, as shown in Figure 1. The kidneys are an essential component of this system that help to filter blood and remove waste from the body in the form of urine. The urine formed by the kidneys is carried to the bladder by long tube-like structures called ureters. The bladder serves as a storage unit for urine. When the bladder is full, the urethra carries the urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. This process is known as micturition. Also, it is important to note that there are two urinary sphincters: the internal urinary sphincter and the external urinary sphincter. The internal urinary sphincter is made of smooth muscle and is under involuntary control. The external urinary sphincter, however, is made of skeletal muscle and is under voluntary control.
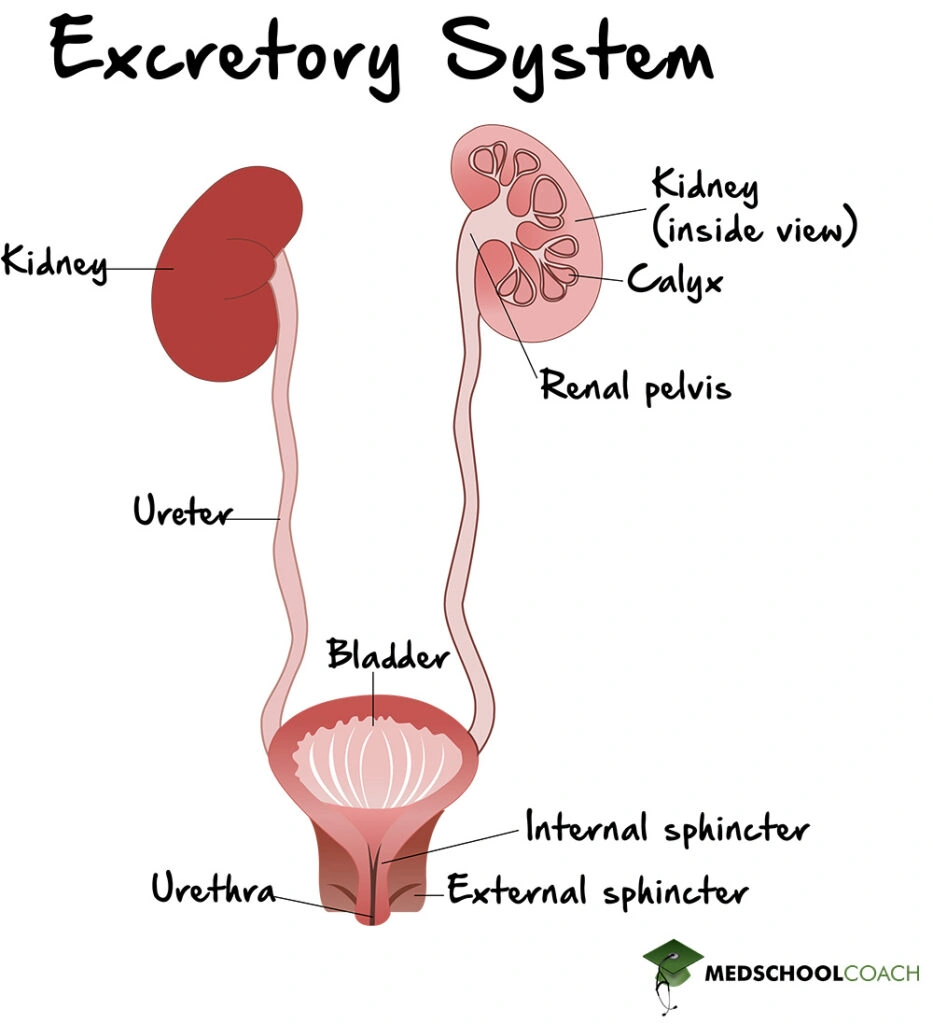
Anatomy of the Kidneys
The kidneys are the central organs of the excretory system. In order to better understand the excretory system, it is therefore important to understand the anatomy of the kidneys and how they connect to the blood supply.
The kidneys receive blood from the renal artery and blood that passes through the kidney is then returned to the body through the renal vein (Figure 2). Moreover, the outer layer of the kidneys is called the renal cortex and the inner part of the kidney is called the renal medulla. The renal cortex is the part of the kidney where filtration of substances such as water, glucose, and amino acids occurs. Also, the hormone erythropoietin, which is involved in red blood cell production is produced in the renal cortex. The renal medulla contains several structures involved in the regulation of salt and water in the body.
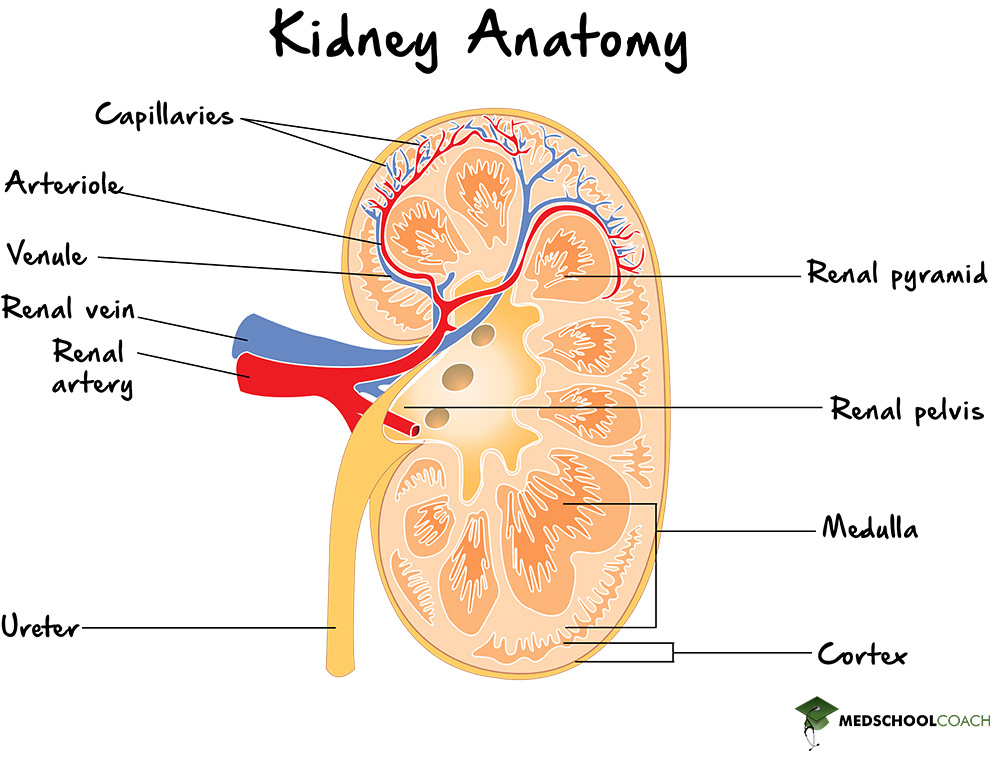
Functions of the Kidney
In addition to kidney anatomy, the MCAT exam will also test your knowledge of kidney function.
The first function, as discussed above, is an excretory function. The kidney eliminates waste from the blood by producing urine. In particular, the kidney removes soluble nitrogenous wastes, salts, as well as excess water from the blood. One consequence of renal disease is the inability to eliminate waste products from the body, which can cause many problems. For example, high potassium can lead to abnormal heart rhythms, and high levels of urea can lead to altered mental status.
A second important function of the kidney is a regulatory function. As the kidneys are producing urine by eliminating wastes and salts, they are also helping to maintain the volume and composition of blood. For example, if the body’s blood volume is low, then the kidneys will decrease urine output to help increase the blood volume until it is back to normal. Likewise, if someone becomes over-hydrated, by drinking too much water, then the blood volume will increase. In this way, the kidneys will increase urine output to decrease blood volume.
The third important function of the kidneys is an endocrine function. As mentioned above, the kidney secretes the hormone erythropoietin that acts on the blood marrow to stimulate the production of red blood cells. It also produces the enzyme renin, which is involved in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system that helps to regulate the body’s blood pressure. Furthermore, the kidneys also help to convert vitamin D produced from the skin into its active form, called calcitriol. Calcitriol helps to increase blood calcium by stimulating calcium reabsorption in the intestines. Calcium is important for bone mineralization. For this reason, an important consequence of long-term, or chronic, kidney disease is the inability to mineralize bone properly, leading to excess fractures or bone pain.
Explore More MCAT Masterclass Chapters
Take a closer look at our entire MCAT Masterclass or explore our Biochemistry lessons below.

One-on-One Tutoring
Are you ready to take your MCAT performance to a whole new level? Work with our 99th-percentile MCAT tutors to boost your score by 12 points or more!
See if MCAT Tutoring can help me
Talk to our enrollment team about MCAT Tutoring

MCAT Go Audio Course
Engaging audio learning to take your MCAT learning on the go, any time, any where. You'll be on the way to a higher MCAT score no matter where you are. Listen to over 200+ lessons.
MCAT Practice Exams
Practice makes perfect! Our mock exams coupled with thorough explanations and in-depth analytics help students understand exactly where they stand.
MCAT Prep App
Access hundreds of MCAT videos to help you study and raise your exam score. Augment your learning with expert-created flashcards and a question banks.
